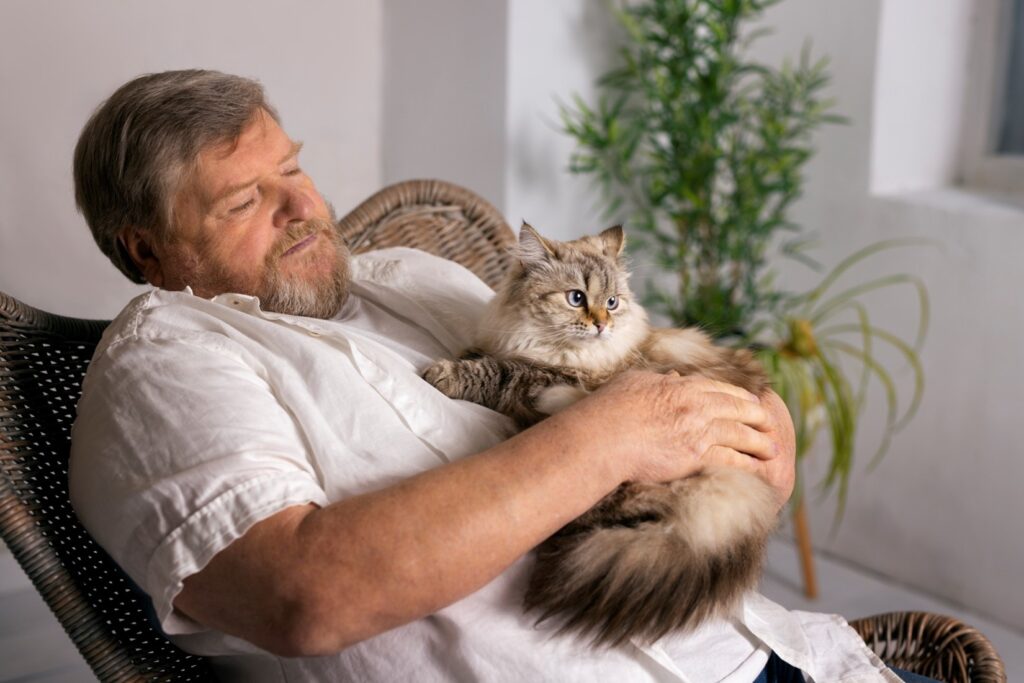
Understanding pet behavior is essential for fostering a positive relationship with your furry companions. By recognizing the root of behavioral issues, you can address them effectively and create a healthier environment for your furry friend. In both cat behavior and dog behavior, issues often stem from internal or external factors, as well as health-related concerns. Let’s dive into the most common causes and solutions for pet behavioral problems.
Common Causes of Behavioral Problems
Pet behavioral issues can be caused by several factors, whether internal or external. Recognizing these can help you address problems more efficiently.
Internal Causes of Pet Behavior Issues
First and foremost, internal factors such as biological, psychological, and cognitive issues can play a significant role in cat behavior and dog behavior. For instance, genetic predispositions or hormonal imbalances may cause your pet to exhibit hyperactivity or impulsivity. Similarly, mental health issues like anxiety or trauma can result in withdrawal, aggression, or even self-destructive behaviors.
Moreover, cognitive challenges, like difficulties with attention or memory, might affect a pet’s ability to follow commands or cope with changes, leading to frustration.
External Causes of Pet Behavior Problems
On the other hand, external factors such as environmental, social, or family dynamics can contribute to your pet’s behavioral issues. For example, a chaotic or stressful home environment may trigger negative behaviors in pets. Additionally, social isolation or peer competition, especially in multi-pet households, can lead to aggression or territoriality. Lastly, family conflicts, inconsistency in training, or an overly strict or lenient approach may exacerbate behavioral issues in both cats and dogs.
Additional Contributing Factors of Pet Behavior
Apart from internal and external pet behavior causes, several other factors can influence dog behavior and cat behavior. These include:
- Fear and Anxiety: Loud noises, new environments, or unfamiliar people can lead to fearful or anxious pet behavior such as hiding, barking, or even aggressive behavior.
- Boredom and Lack of Enrichment: Without proper mental and physical stimulation, pets often develop destructive behaviors, like chewing, scratching, or excessive grooming.
- Health Issues: Pain, discomfort, or aging-related cognitive decline can cause significant shifts in behavior.
- Lack of Training: Insufficient training can even lead to behavioral problems like jumping, begging, or aggression.
- Environmental Changes: Major changes, such as moving to a new house, introducing a new pet, or adjusting daily routines, can cause stress and trigger negative behaviors.

Solutions and Prevention of Behavioral Problems in Pets
Thankfully, many behavioral issues can be managed or even prevented with the right approach. Here are some common problems and how to resolve them.
Excessive Barking
Excessive barking is a frequent issue in dog behavior, often caused by boredom, anxiety, or a need for attention. To address it:
- Mental Stimulation: Keep your dog engaged with interactive toys or puzzles.
- Create a Calming Space: Make sure your dog has a quiet, comfortable area to relax in.
- Professional Help: If the issue persists, seek advice from a veterinarian or animal behaviorist.
Scratching Furniture
In cat behavior, scratching is common as cats mark their territory or release stress. Here’s how to prevent it:
- Offer Scratching Posts: Provide multiple scratching posts in various locations.
- Positive Reinforcement: Reward your cat for using the posts instead of furniture.
- Deterrents: Use double-sided tape or citrus-scented sprays to deter furniture scratching.
Aggression
Aggression can occur in both dog behavior and cat behavior, often due to fear, pain, or lack of socialization. Address it by:
- Consulting a Professional: A veterinarian or animal behaviorist can help pinpoint the cause.
- Positive Reinforcement: Train your pet using rewards to reinforce good behavior.
- Avoid Triggers: Identify and steer clear of situations that provoke aggression.
Separation Anxiety
Pets with separation anxiety may display destructive behavior or excessive vocalization. To alleviate this:
- Gradual Exposure: Slowly increase the amount of time you leave your pet alone.
- Enrichment Activities: Keep your pet occupied with toys or puzzles when you’re away.
- Consult a Veterinarian: For severe anxiety, a professional may recommend further behavioral therapies.
Chewing
Chewing is natural, but it can be destructive. To prevent this in dog behavior:
- Provide Chew Toys: Offer a variety of appropriate chew toys.
- Supervision: Keep an eye on your dog, especially around valuable items.
- Use Deterrents: Apply bitter-tasting sprays on items your dog tends to chew.

House Soiling
House soiling, especially in cat behavior, can be a result of stress or inadequate litter box conditions. To resolve this:
- Check for Health Issues: Visit your veterinarian to rule out medical problems.
- Improve Litter Box Setup: Ensure clean, accessible litter boxes in quiet areas.
- Seek Professional Advice: Persistent issues may require help from a behaviorist.
Importance of Regular Veterinary Check-Ups
Lastly, never underestimate the importance of regular veterinary check-ups. Routine exams can catch underlying health issues that may be affecting your pet’s behavior. At the Animal Hospital of Aurora, we provide a full range of services, from routine exams to surgical procedures, to ensure your pet’s well-being.
In conclusion, addressing behavioral problems in pets requires patience, consistency, and the right approach. With understanding and the proper techniques, you can help your cat or dog lead a happy, balanced life.