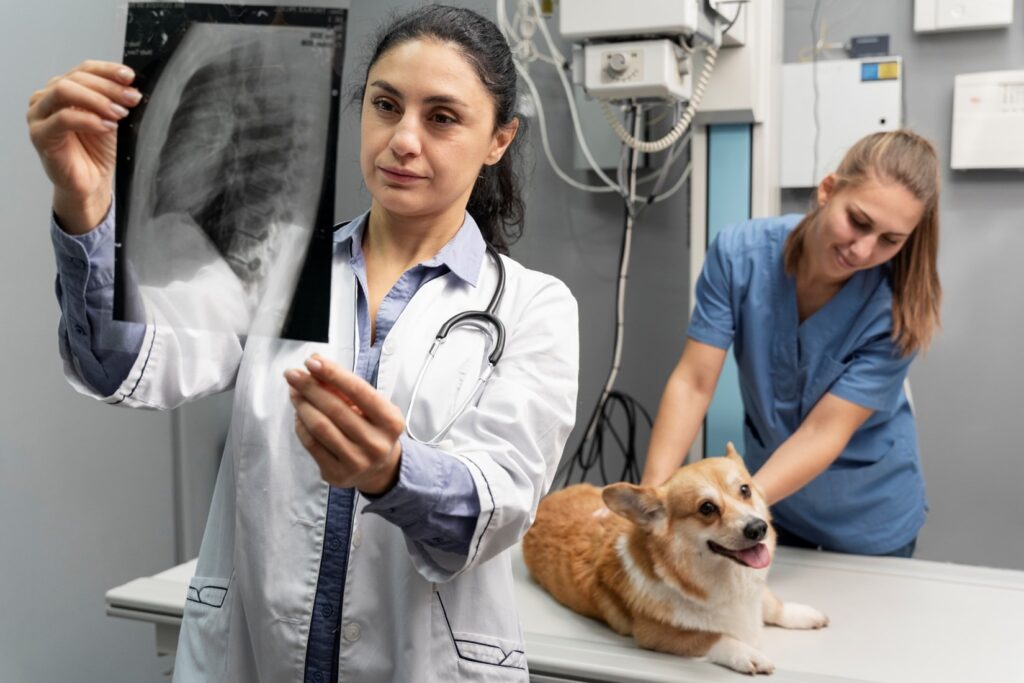
Introduction to Pet Radiography
Radiography, or X-rays, serves as a key diagnostic tool in veterinary medicine. It gives veterinarians a clear view of an animal’s internal structures, helping them diagnose and treat various health conditions. This guide explains pet radiography, its uses, and how it helps keep pets healthy.
What Is Pet Radiography?
Pet radiography uses electromagnetic radiation to create images of an animal’s internal body. X-rays pass through tissues at different rates, showing bones, organs, and other structures. These images appear on a digital detector or film, revealing the animal’s anatomy in detail.
Applications of Animal X-rays
Radiography has many uses in veterinary care, including:
- Bone fractures and dislocations: X-rays can quickly reveal fractures or dislocations and help guide treatment.
- Joint diseases: Veterinarians use radiography to detect and monitor conditions like arthritis and hip or elbow dysplasia.
- Internal organ abnormalities: X-rays can spot problems in the heart, lungs, liver, kidneys, and digestive system.
- Foreign body identification: If a pet swallows an object, radiography helps locate it.
- Tumor detection: X-rays help find tumors, whether benign or malignant.
- Dental examinations: Radiography identifies dental issues like tooth fractures, root canals, and abscesses.

Benefits of Pet Radiography
Radiography offers several advantages:
- Non-invasive: Veterinarians can examine pets without surgery or anesthesia.
- Rapid results: X-rays provide quick answers, leading to fast treatment.
- Cost-effective: Compared to CT scans or MRIs, radiography is more affordable.
- Versatile: Radiography works for various body parts and conditions.
- Safe: Veterinary clinics follow strict safety rules to limit X-ray exposure.
The Radiography Process
The radiography process includes these steps:
- Preparation: The veterinarian sedates or anesthetizes the pet for comfort.
- Positioning: The vet positions the pet on a radiography table for accurate imaging.
- Exposure: The X-ray machine captures the image on a digital detector or film.
- Review: The veterinarian examines the image for signs of disease or injury.
Advanced Radiography Techniques
Veterinarians sometimes use advanced radiography techniques for more detail:
- Contrast radiography: A contrast agent highlights specific organs or structures.
- Fluoroscopy: Continuous X-rays provide real-time images of moving organs or joints.
When Should You Consider Animal X-rays?
You should consider radiography if your pet shows any of these signs:
- Pain or discomfort
- Limping or trouble walking
- Changes in appetite or behavior
- Excessive thirst or urination
- Persistent coughing or sneezing
- Unusual lumps or bumps

At Animal Hospital of Aurora, we use radiography to get a full picture of your pet’s health. Each X-ray tells a part of the story, helping us provide focused treatments.
Conclusion
Pet radiography plays a crucial role in veterinary care. It helps veterinarians diagnose and treat many conditions. By understanding its uses and benefits, you can help ensure your pet gets the best care. If you have concerns about your pet’s health, talk to your vet about whether radiography is right for them.